Patents
U.S. Patent #7,165,962 Web handling roll stand.
Patent granted on January 23, 2007.
|
|
|
Description: A telescoping roll stand for use in an extrusion line includes a linkage connecting one or more auxiliary cooling rolls in a spatial relationship relative to each other and other auxiliary web processing components, including conveyors, load cell rolls, draw rolls, and other web handling components, when one of the auxiliary rolls is shifted in relation to a primary roll. |
|---|
U.S. Patent #8,021,140 Linear bearing assembly to guide movement of roll stand on apparatus for forming an extruded sheet product.
Patent granted on September 20, 2011.
|
|
|
Description: An apparatus for forming an extruded sheet product having an extruder assembly with a sheet die through which flowable material is delivered for sheet product formation and a roll stand assembly with a main frame and a roll stack sub-assembly on the main frame that cause flowable material from the sheet die to be formed into a sheet product. The apparatus further has a sub-frame assembly and a linear slide bearing assembly with at least one rail defining a travel path for the main frame and through which the main frame is guided in movement relative to the sub-frame assembly, thereby to selectively vary relative positions of the sheet die and roll stand assembly along the travel path. |
|---|
U.S. Patent #8,152,509 Gap adjusting mechanism for rolls on a roll stand used in the extrusion forming of a sheet product
Patent granted on April 10, 2012.
|
|
|
Description: A roll stand for use in the extrusion forming of a sheet product from a flowable material having a main frame supporting first and second rolls between which there is a first gap through which at least one sheet layer passes during sheet product formation. A first adjusting mechanism moves the first roll relative to the second roll so as to vary a dimension of the first gap. The first adjusting mechanism has a first element that is moved by a first actuator that is: a) maintained on the apparatus; b) engageable by a hand of an operator; and c) manually movable through an operator's hand to thereby cause repositioning of the first roll. |
|---|
U.S. Patent #8,240,180 Height positioning Mechanism for roll stand assembly.
Patent granted on August 14, 2012.
|
|
|
Description: An apparatus for continuously forming an extruded sheet product having an extruder assembly with a sheet die for delivering flowable material. A roll stand assembly has a main frame with first and second rolls. A vertical height positioning mechanism is operated to vary the relationship between the sheet die and nip location between rolls and has first and second lift components that cooperate with the main frame at first and second laterally spaced locations. The first and second lift components are each movable in first and second opposite paths to selectively elevate and lower the nip location relative to the sheet die. The vertical height positioning mechanism further has an actuating system to selectively and simultaneously cause the first and second lift components to move. |
|---|
U.S. Patent #8,342,118 Sheet coating system on an apparatus for extrusion forming a sheet product.
Patent granted on January 1, 2013.
|
|
|
Description: The anti static coater consists of a non-driven set of nip rolls through which the web passes. The nip roll arrangement contains two 8.0" diameter neoprene rolls each with its own "transfer roll." When the transfer rolls are activated, a sparger tube applies anti-static solution which is spread uniformly by the transfer roll. By closing one or both transfer rolls, coatings can be applied to the top, bottom or both sides of the sheet as required. |
|---|
U.S. Patent #8,490,643 Polymer Valve for diverting polymer during purging for color changeover.
Patent granted on July 23, 2013.
|
|
|
Description: A diverter valve controlling input of two different extruded materials has a valve body having an axially extending opening, and a valve piston axially movable in the opening between first and second positions. The body defines a first inlet for receiving a first material, and a second inlet for receiving a second material with first and second outlets opposite the inlets. The piston has first and second through channels and first and second cross-over channels, each with inlet side and outlet side ports. A first flushing channel communicates with the first inlet and end ports, a second flushing channel communicates with the second inlet and end ports, and a third flushing channel opposite the first two communicates with the second outlet and includes a plurality of ports, with all the ports, inlets and outlets open to the axial opening. |
|---|
U.S. Patent #8,631,925 Adjusting mechanism for rolls on a roll stand assembly.
Patent granted on January 21, 2014.
|
Description: A roll stand assembly for processing a sheet product and having a frame and a plurality of rolls operatively position on the frame so as to define a plurality of nip locations between cooperating pairs of the rolls. The roll axes are substantially parallel with the plurality of rolls operatively positioned on the frame. Two of the rolls are relatively repositionable by guided relative movement therebetween along a first path to vary a gap between the two rolls. The two rolls are relatively repositionable by guided relative movement therebetween along a second path that is different than the first path to vary the gap between the two rolls. A control system is provided through which the two rolls are relatively repositioned by causing guided relative movement between the two rolls in the first and second paths. |
|---|
|
|
U.S. Patent #9,139,393 New Roll Lock-Out Safety System.
Patent granted on September 22, 2015.
|
Description: A roll stand assembly for processing a sheet product with a plurality of rolls on a frame. A first roll has a first sheet engaging surface and a first shaft assembly. A second roll has a second sheet engaging surface and a second shaft assembly. The first and second rolls are relatively movable between: a) an operating relationship; and b) an open relationship. A safety assembly prevents inadvertent changing of the first and second rolls from the open relationship into the operating relationship. The safety assembly includes a first chuck component mounted for movement relative to the frame between: a) a running position wherein the safety assembly is in a disengaged state; and b) a lockout position. |
|---|
 |
U.S. Patent #9,182,067 Chrome Roll Skew Mechanism
Patent granted on November 10, 2015.
|
Description: The pressure required to produce thin PP sheet results in deflecting chrome rolls that lead to thicker gages in the center of the sheet than at the outsides. The chrome roll skew mechanism is designed to utilize this chrome roll deflection in an effort to eliminate such gage variations across the sheet. The bearing assembly mounted to the chrome roll journal is housed within and keyed to an outer housing. The machine direction position of this bearing assembly within the outer housing is controlled by a threaded push/pull device mounted on the front cap of the outer housing. Using this device to adjust one bearing assembly forward and the other backward the same amount will cause the center of the top roll to remain centered over the center of the middle roll while the deflection of the top roll will 'wrap' around the middle roll. |
|---|
 |
U.S. Patent #10,071,517 Polymer filter assembly and method of setting up an extruding system utilizing the polymer filter assembly
Patent granted Sept. 11, 2018
|
A polymer filter assembly through which flowable material from a supply is directed for processing before passing to a die assembly through which the flowable material is delivered to form a sheet layer. The polymer filter assembly has a polymer filter frame that supports processing components for the flowable material and a support assembly for the polymer filter frame. The support assembly includes components cooperating between the polymer filter frame and a base upon which the polymer filter frame is supported to allow controlled relative vertical movement between the polymer filter frame and base to thereby permit controlled alignment between the polymer filter frame and at least one of: a) an upstream component that delivers flowable material from the supply; and b) the die assembly. |
|---|
 |
U.S. Patent #10,207,444 Layer exchange converting technology
Patent granted February 19, 2019.
|
A specialty diverter valve permits exchanging layer sequencing for co-extruded materials, including a split cylinder in the cylindrical opening of a base, each cylinder half being independently pivotable. The base includes first and second inlets for first and second extruded material, and first and second outlets for the material. Base first and second flow paths carry the first and second extruded materials from the inlets to the output openings, and third and fourth flow paths carry extruded material from the first and second first inlet openings to the first and second outlets. The first and second inlet openings and the first and second output openings are axially open to the central opening, and the cylinder halves are adjacent along a plane substantially radial to the central opening axis with each of the cylinder halves including a recess open along the radial plane. |
|---|
 |
U.S. Patent #10,350,810 Barrel assembly and method of setting up an extrusion system utilizing the barrel assembly
Patent granted July 16, 2019.
|
A barrel assembly through which flowable material is delivered to a die assembly through which the flowable material is delivered to form a sheet layer. The barrel assembly has: a conduit having a body with a length defining a lengthwise flow passage between upstream and downstream ends; and a support assembly for the conduit. The support assembly has: a) a conduit engaging assembly; and b) a guide assembly through which the conduit body and conduit engaging assembly are moved guidingly relative to a base, to which the guide assembly is mounted, in a path that is substantially parallel to the length of the conduit body.
|
|---|
 |
U.S. Patent #10,406,738 Die assembly and method of setting up an extrusion system utilizing the die assembly
Patent granted on September 19, 2019.
|
A die assembly through which flowable material from a supply is controllably delivered to a processing assembly at which a sheet layer is formed. The die assembly has a main frame and a support assembly for the main frame. The support assembly includes components cooperating between the main frame and a base upon which the main frame is supported to allow controlled relative vertical movement between the main frame and base to thereby permit con-trolled alignment between the main frame and an upstream component that delivers flowable material from the supply to the die assembly.
|
|---|
 |
U.S. Patent #11,052,592 Extruder assembly and method of extruding a meltable material using the extruder assembly
Patent granted on July 6, 2021.
|
An extruder assembly has a frame with upstream and downstream ends. A barrel assembly on the frame has a passage. At least one material advancing component resides at least partially within the passage and is configured to be turned around an operating axis to thereby cause material to be conveyed from a passage inlet to a passage outlet. A drive assembly turns the at least one material advancing component around its operating axis and has a motor on the frame situated so that at least a part of the motor is in lengthwise overlapping relationship with the barrel assembly. The drive assembly is configured to turn the one material advancing component around its operating axis at speed of at least 300 rpm.
|
|---|
 |
U.S. Patent #11,865,757 Method and Apparatus for Processing a Formable Material / Configurable Rotary Former
Patent granted on January 9, 2024.
|
A method and apparatus for processing a formable material having at least first and second relatively repositionable units. The first unit has a sheet die, with the second unity having a rotary drum with a peripheral forming surface for receiving flowable material from the sheet die. The first and second units can be selectively changed between an operating relationship and a setup relationship, with the latter causing at least one space to be defined/enlarged and within which an operator can maneuver to gain access to a region of at least one of the first and second units. With the first and second units in the operation relationship, moldable sheets can be processed by causing the modable sheets to be applied, and conformed, to the peripheral forming surface on the rotary drum.
|
|---|
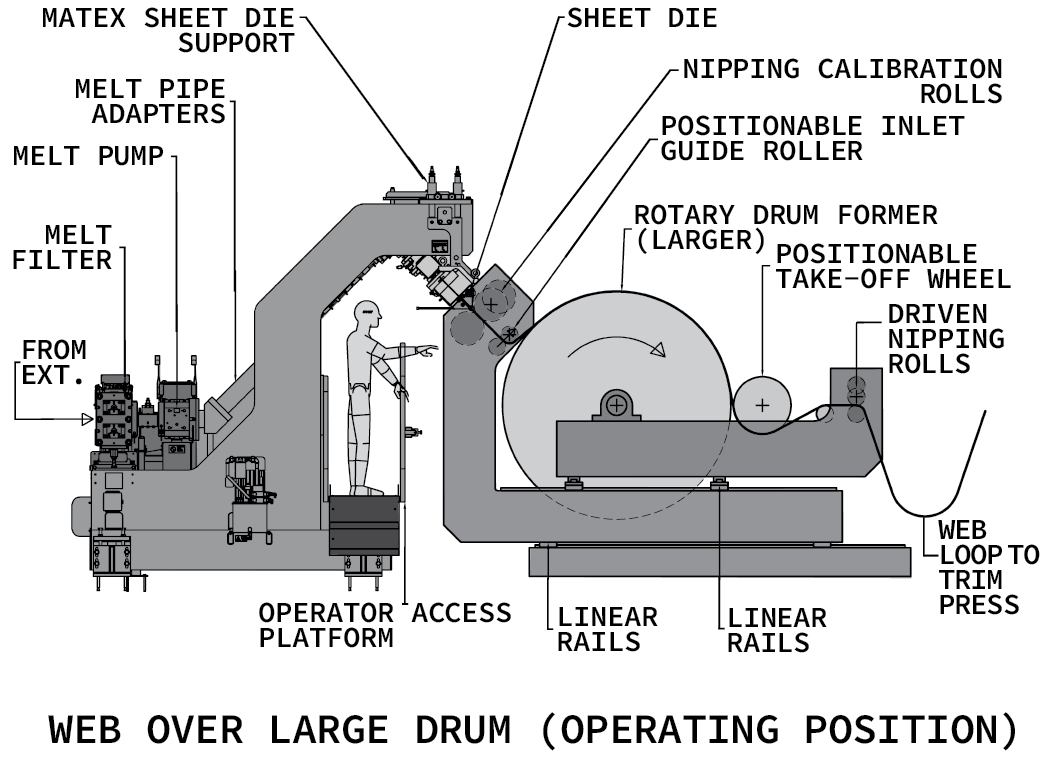 |
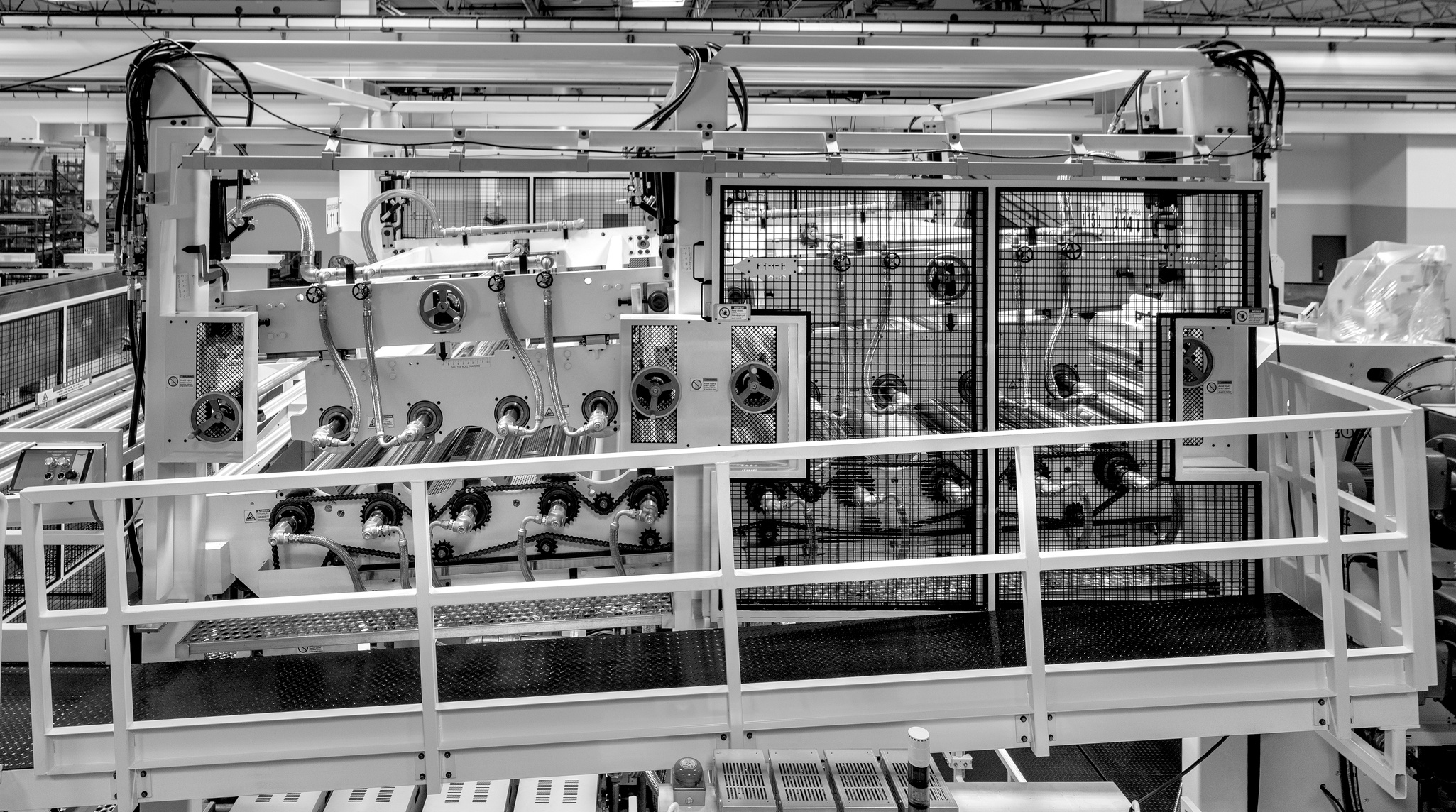
U.S. Patent #11,890,801 Method and System for Processing an Extruded Sheet using a Sheet Conditioning Unit
Patent granted on February 6, 2024.
|
A method and apparatus for processing a heated flexible sheet, with oppositely facing surfaces, that is advanced in a processing path. A first cooling roll has a first peripheral surface for contacting one of the sheet surfaces. A second cooling roll has a second peripheral surface for contacting the other sheet surface. The system is configured so that the first and second cooling rolls are selectively movable in relationship to each other in a manner, other than by moving one or both of the first and second cooling rolls towards or away from the flexible sheet, between: a) a first relationship wherein the first sheet surface is caused to engage the first peripheral surface over a first circumferential extent as the flexible sheet is advanced in the processing path; and b) a second relationship wherein the first sheet surface is caused to engage the first peripheral surface over a second circumferential extent that is different than the first circumferential extent as the flexible sheet is advanced in the processing path.
|
|---|
 |
Trademarks
| PTi® | Reg. No. 3,933,291 | Registered Mar. 22, 2011 |
|
Globaline
G-SERIES® |
Reg. No. 3,685,130
Reg. No. 6,027,322 |
Registered Sept. 22, 2009
Registered April 7, 2020 |
| HVTSE® | Reg. No. 4,677,696 | Registered Jan. 25, 2015 |
|
MultiNIP®
SUPER-G® |
Reg. No.6,198,099
Reg. No.6,208,638 |
Registered Nov. 17, 2020
Registered Dec.1, 2020 |
| REVOLUTION® | Reg. No. 3,041,772 | Registered Jan. 10, 2006 |
| TITAN® PLC Control System | Reg. No. 2,441,713 | Registered Apr. 10, 2001 |
| TRIDENT® | Reg. No. 2,223,616 | Registered Feb. 16, 1999 |
|
|
|
|
|
|